[Effective-Java] Chapter11 #80. 스레드보다는 실행자, 태스크, 스트림을 애용하라
📌 As-is. 직접 구현한 작업 큐(work queue)
Table of Contents
Работа по теме: Effective Java Programming Language Guide - Bloch J. Глава: Table of Contents. Предмет: Программирование. ВУЗ: ТНУ.
studfile.net
참고로 Effective Java 초판의 Item 49에서는 단순한 work queue를 만들어 소개했었다.
- Client 요청 작업을 Background Thread에 위임해 비동기적으로 작업을 처리한다.
- work queue가 필요 없어지면 Client가 queue에 중단을 요청할 수 있다.
- Queue는 남아 있는 작업을 마저 완료한 후 스스로 종료한다.
- Safety Failure나 Dead Lock가 될 여지를 없애는 작업을 수반했었다.
그러나 이제는 이런 코드가 불필요하다.
모든 면에서 더 뛰어난 work queue를 java에서 지원해준다!
📌 실행자 프레임워크(Executor Framework)
Java - ExecutorService를 사용하는 방법
Executors와 ExecutorService를 이용하면 간단히 쓰레드풀을 생성하여 병렬처리를 할 수 있습니다. 어떤 작업들을 병렬로 처리하려면 ExecutorService, SingleThreadExecutor, Future, BlockingQueue를 이용해야 합니다.
codechacha.com
🟡 Executor 실행 : Work Queue 생성
public class Executors {
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool();
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor();
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool();
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
...
}ExecutorService exec = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
// 4개의 스레드를 가진 스레드 풀 생성
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
// submit 메서드로 멀티스레드로 처리할 작업을 예약
// 예약과 동시에 먼저 생성된 4개의 스레드는 작업을 처리
executor.submit(() -> {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Job1 " + threadName);
});
executor.submit(() -> {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Job2 " + threadName);
});
executor.submit(() -> {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Job3 " + threadName);
});
executor.submit(() -> {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Job4 " + threadName);
});
// 더이상 ExecutorService에 Task를 추가할 수 없습니다.
// 실행중인 모든 task가 수행되었다면 스레드풀을 종료합니다.
executor.shutdown();
// shutdown() 호출 전에 등록된 Task 중에 아직 완료되지 않은 Task가 있을 수 있습니다.
// Timeout을 20초 설정하고 완료되기를 기다립니다.
// 20초 전에 완료되면 true를 리턴하며, 20초가 지나도 완료되지 않으면 false를 리턴합니다.
if (executor.awaitTermination(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
System.out.println(LocalTime.now() + " All jobs are terminated");
} else {
System.out.println(LocalTime.now() + " some jobs are not terminated");
// 모든 Task를 강제 종료합니다.
executor.shutdownNow();
}
System.out.println("end");
}- newFixedThreadPool()
- 인자 개수만큼 고정돼 Thread Pool 생성
// 생성
CompletableFuture<String> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
Executors.newCachedThreadPool().submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(2000);
future.complete("Finished"); // 결과 저장
return null;
});
future.get(); // 결과 꺼내기- newCachedThreadPool() :
- 필요할 때, 필요한 만큼 Thread Pool 생성
- 특별히 설정할 게 없고, 작은 프로그램이나 가벼운 server에서 사용하면 좋다.
- 무거운 프로덕션 server의 경우엔 좋지 않다.
- 요청받은 Task들이 Queue에 쌓이지 않고 즉시 Thread에 위임돼 실행된다.
- 가용한 Thread가 없다면 하나 생성하는데, Server가 무거운 경우 CPU 이용률이 100%로 치닫는다.
- 무거운 Server에선 newFixedThreadPool이나 완전히 통제 가능한 ThreadPoolExecutor을 사용하라
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executor.submit(() -> {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Job1 " + threadName);
});
executor.submit(() -> {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Job2 " + threadName);
});
executor.shutdown();
executor.awaitTermination(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("end");
}// 출력 결과
Job1 pool-1-thread-1
Job2 pool-1-thread-1
end- newSingleThreadExecutor()
- Thread 1개인 ExecutorService를 반환한다. (Single Thread에서 동작할 task 처리)
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
Runnable runnable = () -> {
System.out.println("++ Repeat task : " + LocalTime.now());
sleepSec(3);
System.out.println("-- Repeat task : " + LocalTime.now());
};
int initialDelay = 2;
int delay = 3;
// 일정 시간 간격으로 실행
// initialDelay는 처음 실행될 때까지 기다리는 시간
// 완료되는 시간과 무관하게 일정 delay 후 다시 job이 실행된다.
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(
runnable, initialDelay, delay, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private static void sleepSec(int sec) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}- newScheduledThreadPool()
만약, 평범하지 않은 Executor가 필요하다면 ThreadPoolExecutor 클래스를 직접 사용해도 된다.
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService { ... }
🟡 Task 전달
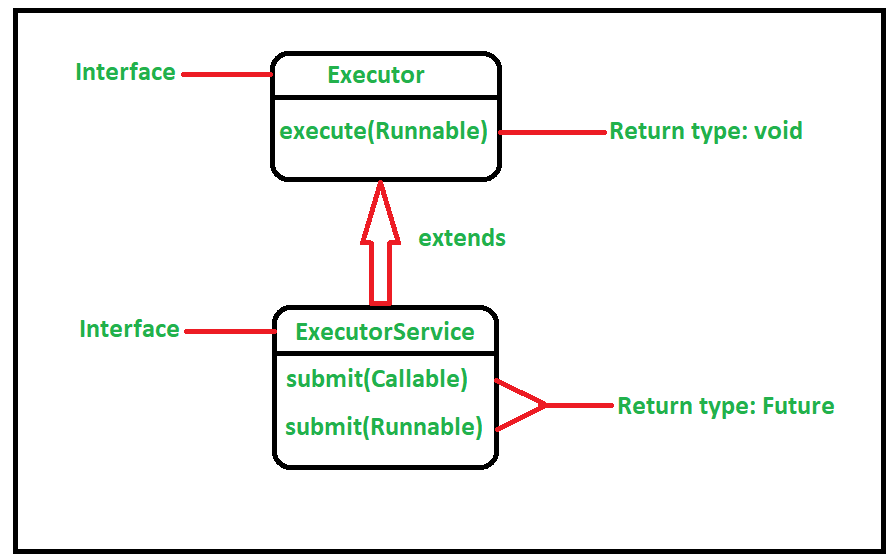
public interface Executor {
/**
* Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
* may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
* thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation.
*
* @param command the runnable task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
* accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
void execute(Runnable command);
}
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
...
}| execute() | submit() | |
| 정의 | Executor Interface | ExecutorService Interface |
| 매개 변수 | Runnable | Runnable, Callable |
| 리턴 타입 | void | Future • 비동기 연산의 결과를 의미 • 실행 결과가 필요할 때 submit() 메서드 사용 가능 • Future 객체의 get() 메서드로 결과를 받을 수 있음 • Future의 get()은 blocking call이므로 주의 • Thread Exception 발생 시, get() 메서드 호출했을 때 발생 |
| 사용 시점 | 결과 상관 없이 Thread Pool의 worker thread에 의해 코드 병렬 실행 | 작업의 결과에 대해 필요할 때 |
exec.execute(runnable);
exec.submit(runnable);
exec.submit(() -> {...});
🟡 Executor 종료
exec.shutdown();해당 작업이 실패하면 VM 자체가 종료되지 않는다.
✒️ ExecutorService의 주요 기능
- Future.get() : 특정 Task가 완료되기를 기다린다.
- invodeAny() / invokeAll() : Task 모음 중 아무것 하나 혹은 모든 Task가 완료되기를 기다린다.
- awaitTermination() : ExecutorService가 종료하기를 기다린다.
- ExecutorCompletionService : 완료된 Task들의 결과를 차례로 받는다.
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor : Task를 특정 시간, 혹은 주기적으로 실행하게 한다.
📌 Thread를 직접 다루는 것을 삼가라
- Thread를 직접 다루면 작업 단위와 수행 메커니즘 역할을 모두 수행하게 된다.
- ExecutorService를 사용하면 작업 단위(Task)와 실행 메커니즘을 분리된다.
- 작업 단위
- Runnable
- Callable (Runnable과 비슷하지만 값을 반환하고 임의의 예외를 던질 수 있음)
- 실행 메커니즘
- ExecutorService : Task 수행 정잭을 선택하고, 언제든지 변경할 수 있다. (Collection Framework가 데이터 모음을 담당하듯, Executor Framework가 작업 수행을 담당해준다.)
- 작업 단위
📌 ForkJoinPool
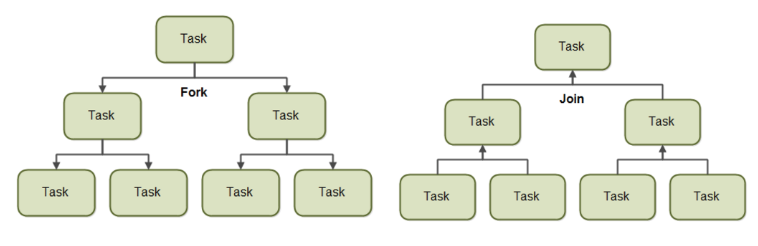
// forkJoinPool 생성 방식 -> 인자로 생성할 스레드 개수 할당
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(4);- ExecutorService와 비슷하다.
- ThreadPool을 생성하여 여러 작업을 병렬처리한다.
- Task의 크기에 따라 분할(Fork)하고, 분할된 Task가 처리되면 합쳐(Join)서 리턴한다.
- ForkJoinPool에서 어떠한 task를 처리하려면 다음의 두 개의 클래스를 사용해야 한다.
- RecursiveAction
- 리턴 값이 없는 Task
- RecursiveTask
- 리턴 값이 있는 Task
- Parent는 Child Task의 리턴 값을 기다려서 합친 후 상위 Parent로 전달한다.
- RecursiveAction